Why does electricity make noise?
The short answer
Electricity makes noise because the alternating flow of electrons creates vibrations in electromagnetic devices. If the device has a component that picks up this vibration, such as a transformer, it causes both the component and the surrounding air to vibrate, producing a humming or buzzing noise.
The long answer
Electrical humming or buzzing can often be heard when you are close to power lines, transformers, or electrical appliances.
To understand why electricity makes noise, we first need to get into how electricity works. In order for an electric current to flow, charges (electrons) must be moving.
In direct current (DC), the charges move in one direction only. In alternating current (AC), however, the charges move in one direction for a very short time and then reverse direction. This continuous cycle of switching directions is known as the frequency, which is measured in Hertz (Hz). In the United States, AC power cycles 60 times per second.
This diagram by Chris Woodford is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0
So now that we know about electricity, what exactly is vibrating to create that electric hum?
What causes the hum of electricity?
Electricity’s hum is typically caused by a magnetic element inside an electrical device. For example, when you're near power lines, you might hear an electric buzzing sound coming from a device called a transformer. A transformer contains an inductor, which is an electromagnet made of a piece of iron with a coil of wire wrapped around it.
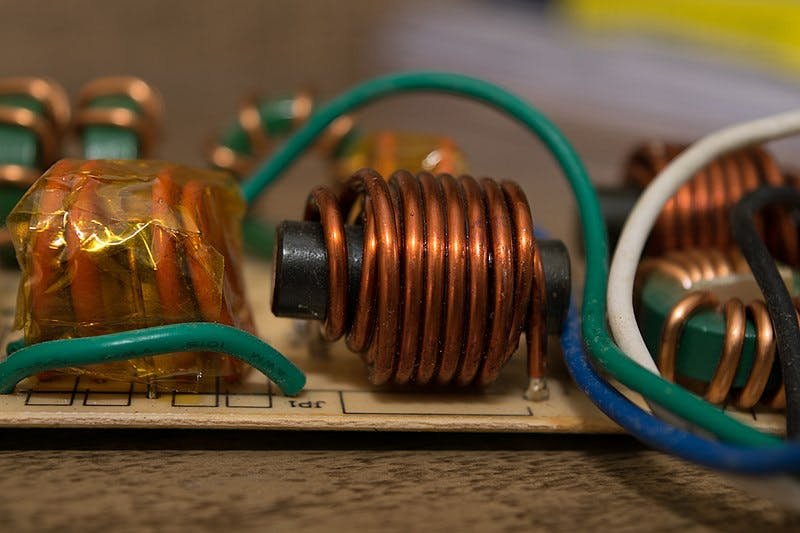
This is an example of a wire-wrapped inductor. "Inductor filter - Line filter " by Marcnovac is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
An inductor vibrates at the frequency of the AC power flowing through it. These vibrations cause the air around the device to vibrate as well. So electricity makes noise because the movement of electrons moving back and forth results in vibrations that become more audible as more surrounding parts vibrate.
Bonus brain points
Does DC power ever produce a sound?
Yes, it's possible for a DC-powered device to hum if it has components that are susceptible to vibrations, such as a DC motor. However the frequencies are much lower, making the hum less noticeable than in an AC-powered device.
Curious about how the world works?
Today You Should Know is a free, weekly email newsletter designed to help you learn something new every Friday.
Subscribe today 👇
Sources
Hamer, A. (2022, January 24). Why does electricity make a humming noise? LiveScience. Retrieved March 5, 2023, from https://www.livescience.com/electricity-humming-noise
Rader, A. (2015, August 22). Electricity & Magnetism | Alternating Current. Physics4Kids.com. Retrieved March 5, 2023, from http://www.physics4kids.com/files/elec_ac.html