Does soap need bubbles to clean?
The short answer
No. Soap bubbles are merely a byproduct of the cleaning process. You don't need bubbles to know that the soap is cleaning effectively.
The long answer
Scrub-a-dub-bub?
It's a pertinent question for those on dish duty: Do bubbles indicate that soap is cleaning effectively?
Let's begin with a quick lesson on how soap works:
How does soap clean?
We all know that oil and water don't mix, which is why it's nearly impossible to clean greasy dishes with just water. That's where soap comes in.
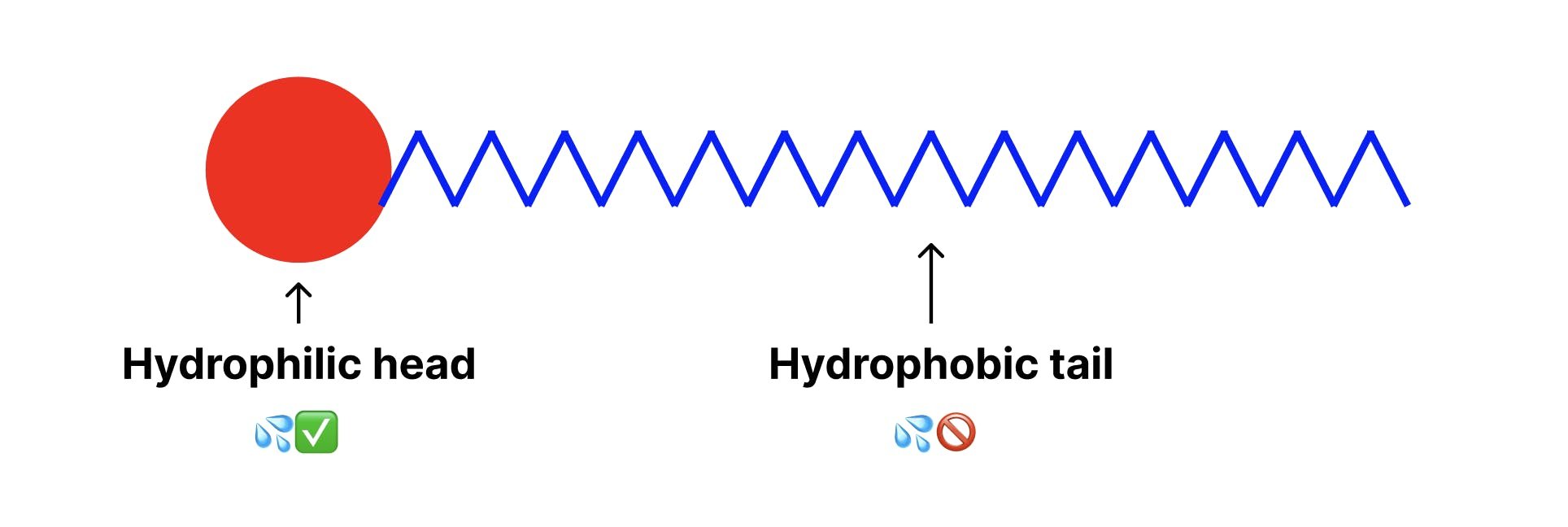
Soap is a substance that attaches to oils and fats, allowing them to be washed away with water. At a molecular level, soap has a hydrophilic head (bonds with water) and a hydrophobic tail (repels water and bonds with oils and fats).
An overly simplistic diagram of a soap molecule.
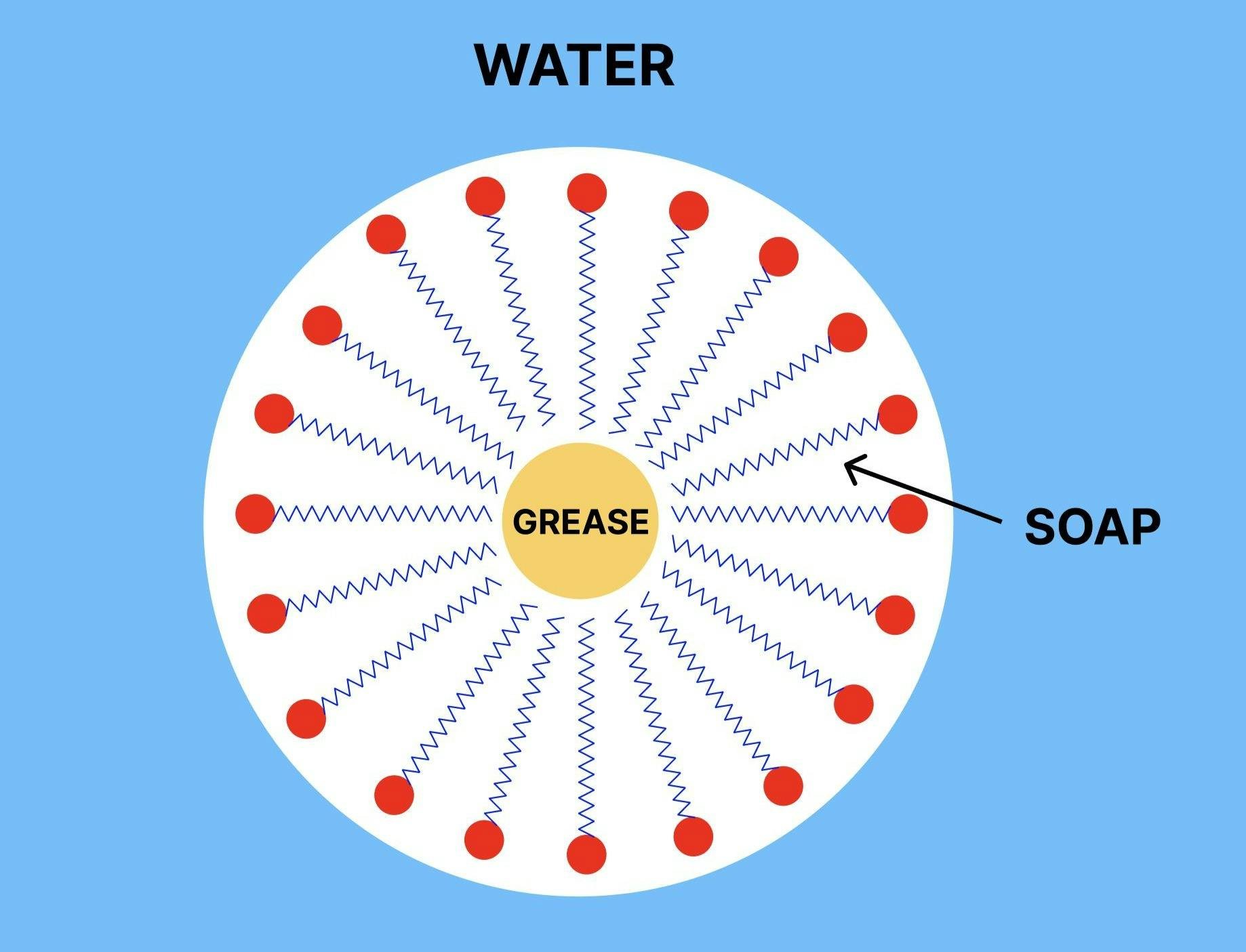
When soap mixes with water and grease, soap molecules form structures called micelles (not to be confused with yourcelles 🥁).
Micelles surround particles of oil and fat, with hydrophobic tails bonding to grease and hydrophilic heads attaching to water.
A diagram of a soap micelle picking up a particle of grease.
Soap essentially suspends grease, allowing it to be washed away with water. Without soap, water alone wouldn't be able to remove the grease so easily.
Does soap need bubbles to clean?
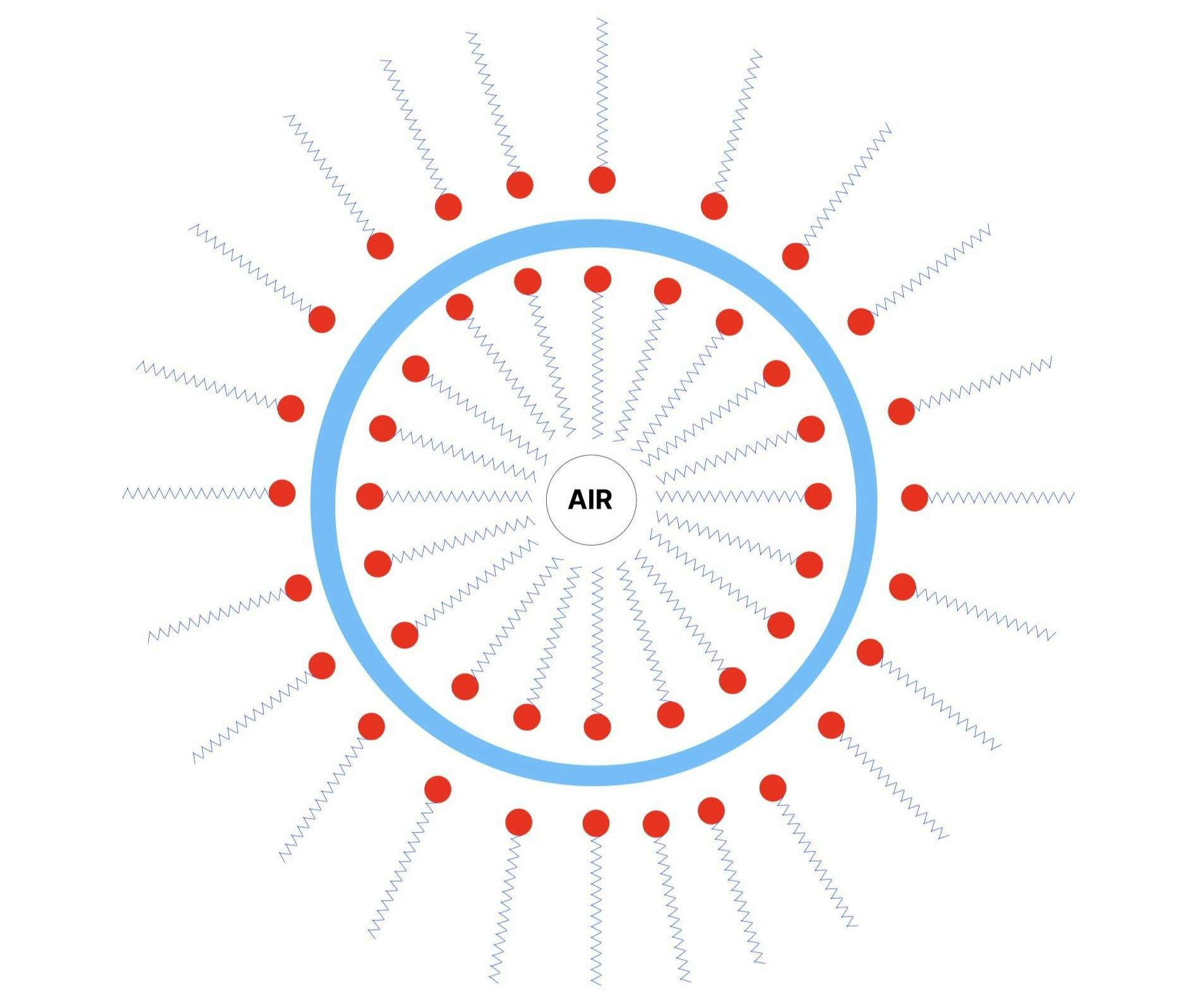
Nope. Soap suds are just a byproduct of the cleaning process. Bubbles form when air gets stuck between soap and water layers.
Designers, please avert your eyes. I didn't know how to make a perfect soap circle in Figma. 😳
Bubbles form easily with soap because it is a natural surfactant, short for "surface active agent". A surfactant reduces the surface tension of water, allowing soap to mix with water and wash away dirt.
With soap's surfactant powers, water becomes more spreadable and prone to forming bubbles. However since soap doesn't need air to attach and lift away grease, bubbles aren't necessary for cleaning.
Interestingly though, many soap and detergent manufacturers add extra surfactants, called sudsing agents, to intentionally create bubbles. This is because consumers associate bubbles with cleaning, so more bubbles make the product seem more effective.
Natural sudsing agents include cocamidopropyl betaine (from coconuts) and octyl glucoside (from the foxglove plant). Common chemically-produced sudsing agents include sodium laureth sulfate and ammonium lauryl sulfate.
🧠 Bonus brain points
What is the difference between soap and detergent?
Soap is made from natural ingredients like plant and animal fats, whereas detergent is synthetic product designed for specific cleaning tasks.
While soap has been around for thousands of years, detergents entered the picture when World War I caused a shortage of soap ingredients. Manufacturers used chemical innovations to meet the demand of soap without requiring highly-sought-after natural ingredients.
Curious about how the world works?
Today You Should Know is a free, weekly email newsletter designed to help you learn something new every Friday.
Subscribe today 👇
Check out some other curious questions:
Sources
American Chemistry Council, Inc. (2022, October 1). Surfactants. Chemical Safety Facts. https://www.chemicalsafetyfacts.org/chemicals/surfactants/
Clean People. (2023, September 21). More Suds Equals More Clean: Fact or Myth?. Clean People. https://www.getcleanpeople.com/more-suds-eqauals-more-clean-fact-or-myth/
Conger, C. (2014, June 13). How Does Soap Work?. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZOKAoNbJkSg
Dropps. (n.d.). Do Suds Help Clean?. Dropps. https://www.dropps.com/blogs/spincycle/do-suds-help-clean
Friedman, I. (2015, April 18). How Does Soap Work?. Chagrin Valley Soap & Salve. https://www.chagrinvalleysoapandsalve.com/blogs/idas-soap-box-blog/how-does-soap-work
Friedman, I. (2018, October 31). How Does Natural Soap Create Lather?. Chagrin Valley Soap & Salve. https://www.chagrinvalleysoapandsalve.com/blogs/idas-soap-box-blog/how-does-natural-soap-create-lather/
Jabr, F. (2020, March 13). Why soap works. Yale School of Medicine. https://medicine.yale.edu/news-article/why-soap-works/
Let’s Get It Clean. (2022, March 9). How Soap Works - 3D Animation. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YnyYsEBJ80I
NBC News Learn. (2020, May 2). It’s a Wash: The Chemistry of Soap. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IHKPLhEb3YM
Page, A. (2009, August 20). What makes soap foam?. HowStuffWorks. https://health.howstuffworks.com/skin-care/cleansing/products/soap-foam.htm
Ticsay, J. (2016, August 18). Simple Science: The Difference Between Soap and Detergent. Nyco Products Company. https://www.nycoproducts.com/resources/blog/simple-science-the-difference-between-soap-and-detergent/
Vivek, S., & Tangirala, S. (2022, April 11). Why do soap bubbles form?. OpenALG. https://alg.manifoldapp.org/read/science-of-everyday-materials-4-11-2022/section/c359dcb0-e64a-4758-b07e-2ed7a7fbfdf5




It’s like an American accent but with calendars.